In this article Show
If you ask us, we would like to compare this situation as you are benign on Earth compared to being in space without a spacesuit.
The world is surrounded by water. Indeed, nearly 75 percent of the earth has numerous saltwater, brackish, turbid, or freshwater sources with varying salinity ratios.
And all these bodies of water are made of living things—many of which we want to keep as animals at home. Various fish species found in oceans, lakes, rivers, and rivers have evolved over millions of years, and long period freshwater has adapted to their preferred environments.
Fish are classified by their resistance to salinity. Stenohalinspecies are classified as fish that can only tolerate minimal amounts of salinity (freshwater fish such as goldfish, saltwater fish such as tuna). The salinity of these species is distinct from that of their natural surroundings in oceans.
Though you may find fish that can live on both fresh and saltwater. Yet, the number is not much. Most of them will suffer if they are put out of their natural habitat. In this article, we will elaborately discuss the Saltwater Fish Response in a Freshwater Aquarium. Let’s get started.
Also worth reading;
- Goldfish Tank Size: How Many Can You Keep in a Small Fish Tank
- What Aquarium Fish Eat Planaria?
- How to Protect Fish Eggs In An Aquarium
- What Aquarium Fish Don’t Have Scales?
- Is Clownfish A Freshwater Or Saltwater Fish?
Popular Saltwater Fishtank Fish
Before knowing about the response, let’s get to know about some famous saltwater fish that are put in aquariums.
1. Clownfish
In nature, they live between anemones, the clownfish cannot bite because they are coated with mucus that covers them. If there are anemones in them, they would do well in aquariums.
They can live in tanks of as little as 10 gallons, but these tanks need more effort to maintain stability and adaptability to fish.
2. Green Chromis
This shiny blue/green fish is popular with novices because it looks great and calm. Green Chromis are often unbelievably hardy, but they need to be served meaty foods numerous times a day since they are carnivores.
3. Pajama Cardinalfish
These fantastic little fish are among the most curious and appropriate for new aquariums on this list. They are very quiet so the more aggressive fish are not necessary because they can be harassed quickly.
4. Yellow Tangs
The Yellow Tang is perhaps one of the most popular and therefore familiar saltwater aquarium fish people. These pretty, lively, yellowfish have strange little faces and peculiar characteristics.
5. Bicolor Blenny
These little fish are normally very quiet but some smaller fish such as gobies and dartfish, or fleshy coral polyps, may be picked. In wider environments, not so much the smaller ones – they do well, like coral tanks.
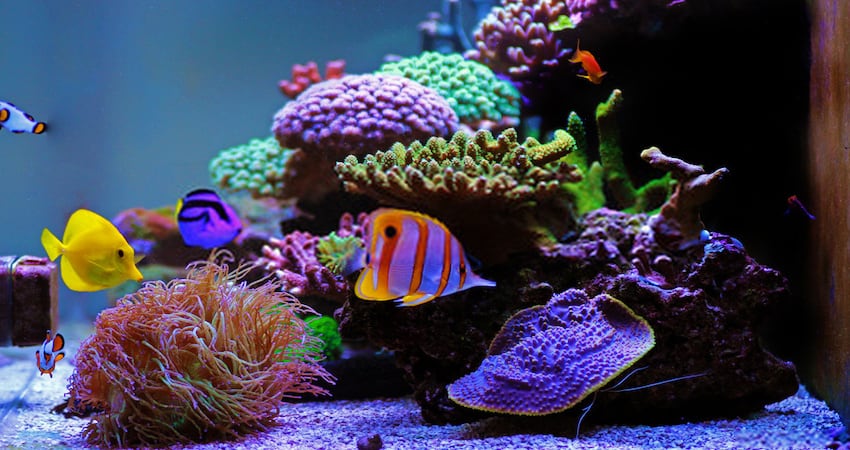

Popular Freshwater Fishtank Fish
Freshwater fish are more popular among aquarium owners for their easy maintenance. Here are some popular freshwater fish for the aquarium;
1. Guppies
Guppies are a species of fish that makes great animals for beginners. They are incredibly easy to look after but prefer to breed easily if the species are not segregated.
2. Betta Fish
Betta fish, particularly males, are known for their highly territorial, highly aggressive nature. You can store your Betta Fish with other fish species in a big tank if it is peaceful enough.
3. Cory Catfish
These catfish are one of the best in the general populace – they live in a huge array of environments, get along with (almost) other animals, and are active and enjoyable.
4. Swordtails
Male Swordtails are designed to give them their names, with an odd “sword” sticking out of their tails. This unique aspect makes you a very attentive person in every aquarium in the community. Much like other living bearers, in a wide variety of conditions, Swordtails are easy to sustain and prosper.
5. Goldfish
For beginners and experienced aquarium enthusiasts, Goldfish is a wonderful freshwater product. They are comfortable in a 40-gallon fish tank and can be up to 18 inches in height. Tetris, discus, guppies, and rainbow fish are all quite well received.
Popular Fresh And Saltwater Fish
As we mentioned earlier, some fish can live or survive in both salt and freshwater. They are versatile enough in both freshwater and saltwater aquariums to survive. These fish are highly resistant to salinity levels and are exceptionally adapted to the two environments. Here is a list;
1. Gulf sturgeon
These primitive fish live from Louisiana to Florida, in summer, in the tidal rivers, and in winter, in the aquatic environments of the Gulf of Mexico. Adult sturgeons are mainly found in saltwater but return to the inland rivers in which they started to breed.
2. Green Sawfish
The sawfish, which is critically endangered, comes from the Indo-West Pacific region. It likes low tides and regular estuaries and channels. The fish was found 150 miles from the coast in Australia’s Northern Territory, with significant moving distances inland.
3. Sockeye Salmon
Sockeyes are born in the inland rivers, like most salmon species, but they spend most of their lives in Pacific Ocean waters. They only spawn once in their ancestral rivers and then die.
4. Barramundi
The Barramundi is a catadromatic fish found in the Indo-West Pacific, also known as Assytic sea bass. This species survives primarily on sweet-water rivers but migrates downstream to mate and spawn at the beginning of the monsoon.
5. American Eel
American eels begin their lives in the middle of the Sargasso Sea like eggs. The small larvae then are washed off by sea streams on the US coast where they migrate downstream into freshwater lakes and rivers.
Fresh Water Effect On Saltwater Fish
The reason some fish typically live in freshwater while others live in seawater is that any habitat gives them typical opportunities to thrive. As the trend or hobby of aquarium become famous, pet fish owners become more concerned about the fact of keeping saltwater fish in their tank as they are more unique and colorful.
In a salt-deficiencies environment, the poultry fish retain physiognomy, helping them to focus salts in their bodies, while the marine fish, in a hypertonic environment, excrete excess salts. Fish who live on both sides maintain both mechanisms.
Tropical or saltwater fish are purely marine non-freshwater saltwater fish. These fish are reef-related fish that live in the reefs. In a few minutes, you place saltwater fish in the freshwater, because they can die.
A saltwater fish helps to osmose in freshwater. The strain used to inhibit the chemical movement of water through the semi-permeable membrane is osmotic pressure. The osmotic pressure increases as water flows into a higher concentrated solution by a semi-permeable membrane.
Saltwater fish cannot survive in freshwater, since their bodies are strongly concentrated in salt solutions (too much for freshwater). Water flows through your body until you eventually bloat and die all your cells make up too much water.
Also euryhaline fish require an acclimatization phase or time to adapt to another salinity as they migrate to a new area. The euryhaline fishery can balance the salt concentrations between their bodies and their climate by mixing the salinity of multiple environments with different stages of life.
Tank Habitat Decor For Saltwater Fish
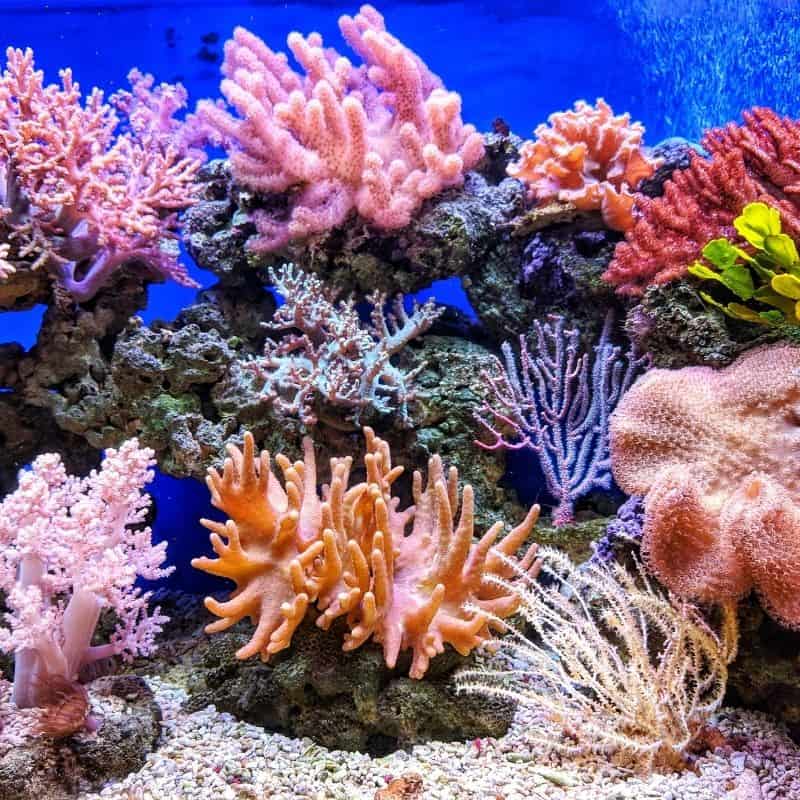

Saltwater fish are typically introduced from all over the world from native fish from the ocean. Fish in saltwater requires a special setting that combines stable temperatures and water conditions.
Oceans appear to remain the same most of the time and adjust very slowly if any. regardless of their scale. So you have to provide them with the proper environment to live in and adjust to. Let’s know them;
1. Demersal Zone in Fishtank
The demersal zone is a portion of the sea or ocean (or deep lake) that consists of the water column between the sea bed and benthos (and which is greatly influenced by it).
The Demersal field, also called groundfish, is located right above the Benthic zone and forms a shelf in the broader deep zone. on or around sea or lake floors (the demersal zone). They inhabit the floors of the sea and lake beds usually made up of dirt, sand, gravel, or stone.
So, if you intend to keep this kind of fish you have to make sure that, you have decorated your fish tank with dirt, sand, gravel, or stone.
2. Coral Habitat Zone
Many aquarium owners wish to have Coral in their fish tanks as they are beautiful to watch and colorful. Bear in mind that a significant amount of time is required to create reef aquariums. You’ll have a wonderful, stable ecosystem in one year.
Knowledge, goods, and knowledge are now accessible over time and with several successful and ineffective tests. Too many corals in even small, micro, and nano aquariums can now be successfully preserved.
3. Pelagic Habitat Zone
The pelagic field consists of the open ocean’s water column which can be further separated by depth into territories. The word ‘pelagic’ derives from the Greek ancient ‘pelagos’ and ‘free sea.’
Hypothetical cylinders or water column that stretches almost from the sea surface to the ground may think of the pelagic region. Pelagic fish remain in the pelagic environment of the waters of the ocean or lake, not near the land or the surface. Contrary to demersal fish, which dwell on or at the bottom of the coral reef fish.
Making a Pelagic Zone would not be easy in an aquarium. You probably need a large fish tank. And by large we mean very large. And you also have to choose your fish accordingly.

4. Benthic Zone Habitat
About 70% of the earth’s surface covers benthic ecosystems. Ninety-eight percent of aquatic animals live on or on the seafloor. So we may assume that the Benthic Field is almost Demersal Zone duplicate.
The low temperature and high pressure characterize this area. These conditions are not suitable for the protection of extensive flora and fauna in the region. The benthic sediment layers tend to recover nutrients that help the water life in the upper column to survive.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does salt water affect freshwater fish?
Special cells in their gills are used to use freshwater peaches to take salts, such as chloride, and lose their water to keep their body salty. If fish are under heat, adding salt to the water doesn’t mean they waste too much salt.
Why do saltwater fish die in freshwater?
Saltwater fish cannot live in freshwater because they have a high concentration of salt solution in their bodies (too much for freshwater). Water will flood through the body until all the cells will absorb so much water they would finally bloat and die.
Sea fish surviving in freshwater?
Some species of fish can live in saltwater and freshwater. These species are referred to as fish with euryhaline. Many species of fish can however only live based on their ability for salinity or the amount of salt they can do within their bodies.
Can Guppies be kept in saltwater?
Yes, in saltwater guppies can live. Up to 150% of seawater salinity can be accepted by the guppies.
Can I add salt to a freshwater aquarium?
Start as a guideline, with 5 gallons of aquarium water, with one tablespoon of salt. For both fish and trees, this is a healthy dose. Watch the every 24 hours the aquarium. If the dose of salt does not increase, it can replicate for up to four days.
Conclusion
In many species, the majority of the fish can only exist based on their immunity to salinity, or based on the number of salts that can be handled by their bodies.
Make sure that the aquarium is not suddenly altered in salinity, even risking euryhaline. The goal of this article is to give you an informative look at the impacts of freshwater on saltwater fish.
Ultimately, fresh or brackish seawater is suited to or populated by fish. Since any area gave the various species a competitive advantage.