In this article Show
As an experienced fishkeeper, I’ve noticed a common query popping up in forums and discussions: why do these graceful creatures sometimes spend a lot of time in one corner of their tank? It might seem like a simple behavior, but it can be a window into understanding your betta’s health and well-being.
In this article, we’ll explore the various reasons behind this behavior. From the intricacies of their environment to the subtleties of their health, we’ll look at what might cause your betta to prefer one corner and what you can do to ensure they’re happy and healthy in their aquatic home.
Why Does My Betta Fish Stay In The Corner?
The main reason why betta fish often stay in corners is typically due to stress or discomfort arising from their environment. Factors such as poor water quality, unsuitable tank mates, inadequate tank size, or health issues like disease can lead to this behavior. Ensuring optimal tank conditions, including regular water changes, appropriate filtration, and a calm, enriched habitat, is crucial for your betta’s well-being.
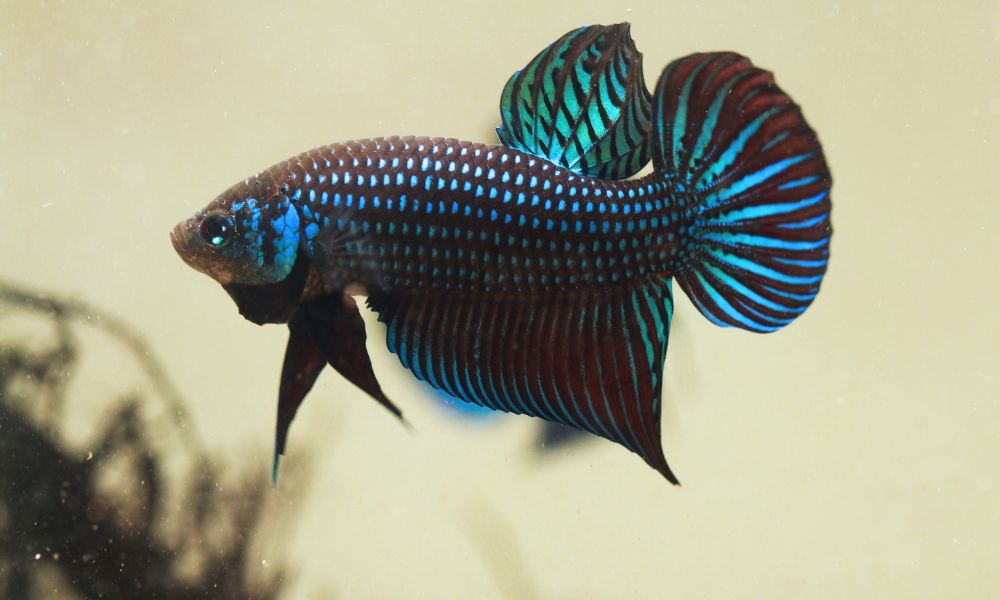

Possible Reasons Why Betta Fish Stay in Corners
1. Stress Factors
Betta fish are sensitive to their environment, and stress plays a significant role in their behavior. Poor water quality, often indicated by imbalanced pH levels or high ammonia and nitrite concentrations, can cause significant stress.
Similarly, inappropriate tank mates can be a source of constant anxiety for bettas, known for their territorial nature. Abrupt environmental changes, such as sudden light shifts or temperature fluctuations, can also lead to stress. When stressed, bettas may retreat to a corner as a coping mechanism, seeking a sense of security in a more confined space.
2. Health Issues
Health concerns are another critical reason why a betta might stay in a corner. Diseases like fin rot, bacterial infections, or parasitic attacks can cause discomfort, leading them to isolate themselves.
Conditions such as swim bladder disorder, which affects their buoyancy and swimming ability, may also make it difficult for them to swim around freely, resulting in them spending more time in one spot. Monitoring your betta for signs of illness, including changes in appetite, color, or activity levels, is essential to address these health issues promptly.
3. Tank Environment
The setup of a betta fish tank greatly influences its behavior. A small or overcrowded tank can cause stress due to limited space and lack of hiding spots. Bettas thrive in environments that mimic their natural habitat, which includes ample space to swim and areas to hide or rest, like plants or caves.
A tank lacking these elements might lead your betta to seek shelter in a corner, which can appear to them as a safe spot. Ensuring the tank is adequately sized, with a balanced layout of open swimming areas and hiding places, is crucial for their well-being.
Improving Your Betta’s Environment
Creating an ideal environment for your betta fish is crucial for their health and happiness. Here are some recommendations and guidelines:
1. Tank Modifications
- Plants: Live or high-quality artificial plants not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the tank but also provide essential hiding spots for your betta. Plants like Anubias or Java Fern are excellent choices as they don’t have sharp edges that could harm delicate betta fins.
- Hiding Places: Adding caves or decorations with smooth openings allows your betta to explore and rest. Ensure these are free from rough textures to prevent fin damage.
- Appropriate Tank Mates: Bettas are known for being territorial, especially males. If you choose to have other fish in the tank, select peaceful species that do not nip fins or compete aggressively for territory. Snails or small shrimp can be good companions, but always observe how your betta interacts with them.
2. Maintaining Optimal Water Quality
- Regular Water Changes: Perform partial water changes weekly to keep the water clean and free from harmful toxins. This helps in maintaining a stable pH level and reducing nitrate buildup.
- Filtration: Use a high-quality filter that is appropriate for the tank size. It should be gentle enough to not create strong currents, as bettas prefer calm waters.
- Water Testing Kits: Regularly test your water for pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels. Ideal conditions for bettas include a pH between 6.5 and 7.5, and ammonia and nitrite levels at 0 ppm.
3. Optimal Temperature Control
- Heater: Betta fish require a warm, stable environment. A heater is necessary to maintain a consistent temperature between 76°F to 80°F (24°C to 27°C).
- Thermometer: Monitor the tank temperature with a reliable aquarium thermometer. Fluctuations outside the ideal range can stress your betta and lead to health issues.
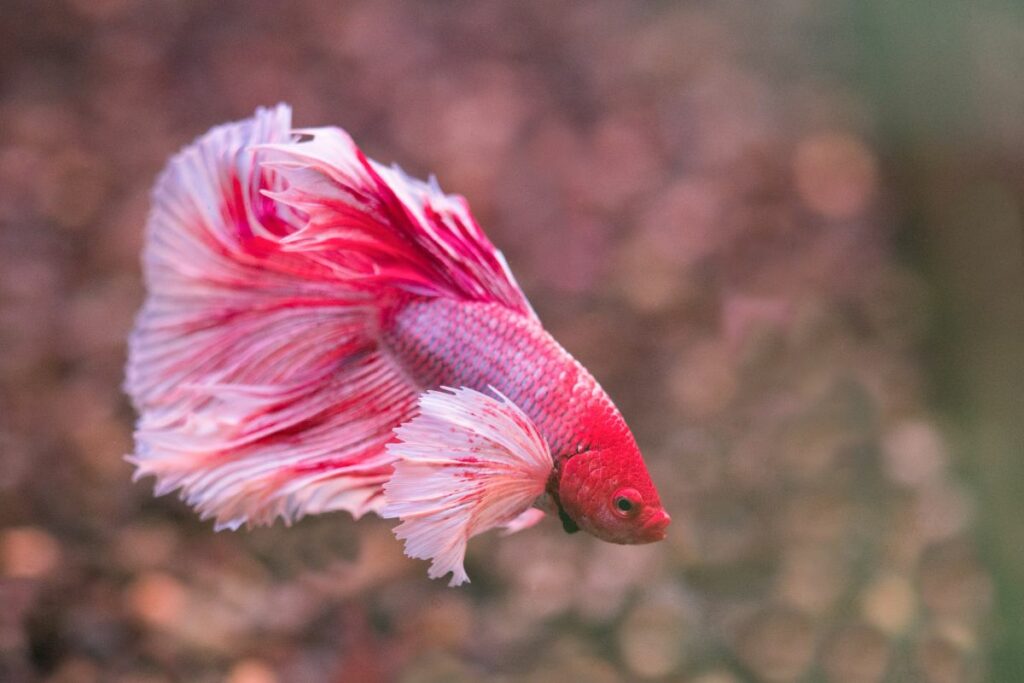

Preventative Measures for Betta Fish Health
Maintaining the health of your betta fish requires consistent care and attention. Here are some preventative measures to ensure your betta remains healthy and stress-free:
1. Consistent Water Quality Management
- Regularly change part of the tank water, ideally 20-25% every week, to keep the water clean and balanced.
- Use a water conditioner to remove harmful chemicals from tap water during each water change.
- Monitor water parameters such as pH, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates with a testing kit, ensuring they remain within safe levels for bettas.
2. Appropriate Feeding Practices
- Feed your betta a high-quality diet specifically formulated for bettas, which typically includes a mix of pellets and frozen or live foods like brine shrimp or daphnia.
- Avoid overfeeding; a good rule of thumb is to feed an amount they can consume within two minutes, once or twice a day.
- Vary their diet to ensure they receive all necessary nutrients and to keep them engaged and interested in their food.
3. Tank Maintenance
- Keep the tank clean by regularly removing any uneaten food, debris, or waste to prevent the buildup of harmful toxins.
- Ensure the filter is functioning correctly and clean it as per the manufacturer’s guidelines without disrupting the beneficial bacteria essential for a healthy tank ecosystem.
4. Stress Reduction
- Provide a tranquil environment with minimal loud noises or disturbances.
- Use dimmed or natural lighting to mimic their natural habitat and maintain a regular light-dark cycle to avoid stress.
5. Regular Health Checks
- Observe your betta daily for any signs of stress or illness, such as changes in color, appetite, activity level, or appearance.
- Look out for signs of common betta illnesses, like fin rot or white spot disease, and seek immediate treatment if necessary.
6. Environmental Enrichment
- Add plants, caves, and other safe decorations to provide hiding spots and stimulate natural behaviors.
- Occasionally rearrange the tank setup to provide a new environment for exploration, keeping your betta engaged and active.
By following these preventative care routines, you can significantly reduce the risk of health problems and ensure your betta fish leads a long, happy, and stress-free life in its aquatic home.